Pure Language Processing (NLP) is the sphere of synthetic intelligence that focuses on the interplay between computer systems and human language. It includes a sequence of levels or phases to course of and analyze language information. The principle phases of NLP will be damaged down as follows.
We work together with language every single day, effortlessly changing ideas into phrases. However for machines, understanding and manipulating human language is a posh problem. That is the place Pure Language Processing (NLP) is available in, a area of synthetic intelligence that empowers computer systems to grasp, interpret, and generate human language. However how precisely do machines obtain this feat? The reply lies in a sequence of distinct phases that type the spine of any NLP system.
Pure Language Processing (NLP) is a department of synthetic intelligence that focuses on enabling computer systems to grasp, interpret, and generate human language. NLP includes a number of levels or phases, every of which performs a vital function in reworking uncooked textual content information into significant insights. Under are the standard phases of an NLP pipeline:
From Understanding to Motion
These phases aren’t all the time utterly separate, they usually usually overlap. Moreover, the particular strategies used inside every part can fluctuate vastly relying on the duty and the chosen method. Nevertheless, understanding these core processes offers a vital window into how machines are starting to “perceive” our language.
The facility of NLP lies not simply in understanding, but in addition in performing upon what it understands. From voice assistants and chatbots to sentiment evaluation and machine translation, the functions of NLP are huge and quickly increasing. As NLP know-how matures, it can proceed to revolutionize how we work together with machines and unlock new prospects in practically each side of our lives.
Phases of Pure Language Processing
1. Textual content Assortment
Instance: Gathering buyer opinions, tweets, or information articles.
Description: This is step one, the place information is collected for processing. It could embody scraping textual content from web sites, utilizing out there datasets, or extracting textual content from paperwork (PDFs, Phrase information, and many others.).
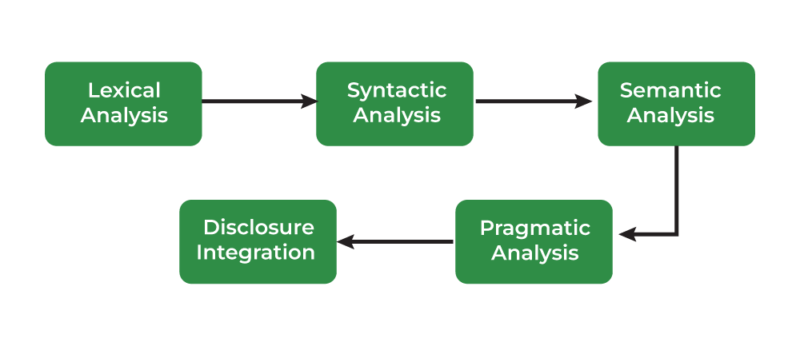
Lexical Evaluation, The Basis of Understanding: This primary part is all about breaking down the uncooked textual content into its fundamental constructing blocks, like phrases and punctuation marks. Think about it like sorting Lego bricks by coloration and dimension.
-
- Stemming/Lemmatization: These strategies cut back phrases to their root types, serving to to group comparable phrases collectively. “Working” and “ran” would each be lowered to “run.” Stemming is an easier method that simply chops off endings, whereas lemmatization takes into consideration the context and produces dictionary-valid base types.The uncooked textual content information is commonly noisy and unstructured, so preprocessing is step one to scrub and format it for additional evaluation. Lemmatization: Much like stemming however extra subtle, it includes lowering phrases to their lemma (e.g., “higher” to “good”).
-
- Tokenization: This step includes splitting a textual content into particular person items known as “tokens.” These tokens could possibly be phrases, punctuation, numbers, and even particular person characters relying on the applying. For instance, the sentence “The cat sat on the mat.” could be tokenized into [“The”, “cat”, “sat”, “on”, “the”, “mat”, “.”].
-
- Cease Phrase Elimination: Frequent phrases (e.g., “the”, “is”, “and”) that don’t contribute a lot which means are sometimes eliminated.Many widespread phrases, like “the,” “a,” “is,” and “of,” don’t contribute a lot to the which means of a sentence. This step removes these “cease phrases” to cut back noise and enhance processing effectivity.
-
- Lowercasing: Changing all textual content to lowercase to keep away from distinguishing between “Apple” and “apple.”
-
- Eradicating Punctuation: Eliminating punctuation marks as they don’t usually add worth for a lot of NLP duties.
-
- Stemming: Lowering phrases to their base or root type (e.g., “operating” to “run”).
2. Textual content Illustration
After preprocessing, the subsequent step is to transform textual content right into a format that may be fed into machine studying algorithms. Frequent strategies embody:
-
- Bag of Phrases (BoW): A easy mannequin the place every phrase is handled as a characteristic, and the textual content is represented by the frequency of phrases.
-
- TF-IDF (Time period Frequency-Inverse Doc Frequency): Weighs the significance of phrases by contemplating their frequency in a doc relative to their frequency in your entire corpus.
-
- Phrase Embeddings: Methods like Word2Vec, GloVe, and FastText symbolize phrases as dense vectors in a high-dimensional area, capturing semantic which means.
-
- Contextualized Embeddings: Fashions like BERT, GPT, and ELMo present dynamic embeddings primarily based on context, providing extra correct phrase representations.
-
- Description: Changing textual content right into a numerical format that machine studying fashions can perceive. Standard strategies embody:
-
- Instance: The sentence “I really like pure language processing” could be transformed right into a vector that represents its semantic which means.
3. Syntactic Evaluation: Understanding Sentence Construction
Phrase Sense Disambiguation: Analyzing the grammatical construction of sentences to grasp how phrases are associated. The result’s usually represented as a parse tree or a dependency tree.Many phrases have a number of meanings. This step goals to establish the proper which means of a phrase primarily based on its context. For instance, contemplate the phrase “financial institution.” Is it a monetary establishment or the sting of a river? For the sentence “The cat sat on the mat,” syntactic evaluation would decide the relationships between “cat,” “sat,” and “mat.
Named Entity Recognition (NER): This includes figuring out and classifying named entities within the textual content, similar to folks, organizations, places, and dates. This enables the system to extract key parts from a textual content and set up data.
Semantic Relationship Extraction: This course of focuses on uncovering the relationships between these entities. For instance, understanding that “Apple” is a “firm” and that “Steve Jobs” was its “founder.” This helps perceive the connections throughout the textual content.
-
- Half-of-Speech (POS) Tagging: This includes figuring out the grammatical function of every phrase in a sentence, similar to noun, verb, adjective, and many others. For instance, in “The cat sat”, “The” is a determiner, “cat” is a noun, and “sat” is a verb. Description: Figuring out the grammatical elements of a sentence, similar to nouns, verbs, adjectives, and many others. This helps in understanding the syntactic construction of the sentence.
-
- Instance: Within the sentence “The cat runs quick,” “The” is a determiner, “cat” is a noun, and “runs” is a verb.
-
- Parsing: This deeper evaluation determines how phrases are grouped to type phrases and sentences. It constructs a parse tree that highlights the relationships between phrases in response to grammar guidelines. This helps the system perceive the underlying construction of the sentence.
-
- Dependency Parsing: This builds on parsing by figuring out how phrases rely upon one another. As an example, in “The cat ate the fish,” “ate” is the principle verb and “cat” is its topic, whereas “fish” is its object.
4. Semantic Evaluation
This part focuses on understanding the which means of phrases, phrases, and sentences.
-
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Figuring out correct names, similar to folks, organizations, places, dates, and many others. Figuring out entities within the textual content similar to names of individuals, locations, organizations, dates, and many others. Within the sentence “Apple introduced a brand new product in New York on January 15,” “Apple” is a corporation, “New York” is a location, and “January 15” is a date.
-
- Phrase Sense Disambiguation: Figuring out the which means of a phrase primarily based on its context (e.g., distinguishing between “financial institution” as a monetary establishment and “financial institution” because the facet of a river).
-
- Coreference Decision: Figuring out which phrases or phrases discuss with the identical entity in a textual content (e.g., “John” and “he”).
-
- Semantic Position Labeling: Assigning roles (e.g., agent, affected person, purpose) to phrases in a sentence to grasp their relationships.
5. Pragmatic Evaluation
This part includes understanding the broader context of the textual content, together with implied which means, sentiment, and intent.
-
- Sentiment Evaluation: Figuring out whether or not the textual content expresses a optimistic, adverse, or impartial sentiment.
-
- Intent Recognition: Figuring out the purpose or goal behind a textual content, particularly in duties like chatbots and digital assistants (e.g., is the consumer asking a query or making a command?).
-
- Speech Acts: Recognizing the perform of an announcement (e.g., is it an assertion, query, request?).
6. Discourse Evaluation: Past Single Sentences
Discourse evaluation includes understanding the connection between sentences or components of the textual content in bigger contexts, similar to paragraphs or conversations.
-
- Coherence and Cohesion: Making certain that the textual content flows logically, with correct hyperlinks between concepts and sentences.
-
- Matter Modeling: Figuring out the principle themes or subjects inside a group of paperwork (e.g., Latent Dirichlet Allocation, or LDA).
-
- Summarization: Lowering a doc or textual content to its important content material, whereas sustaining its which means. This may be extractive (choosing components of the textual content) or abstractive (producing a brand new abstract).
-
- Description: Understanding the construction and coherence of longer items of textual content. This part includes analyzing how sentences join and movement collectively to type a coherent discourse.
-
- Instance: Understanding that in a narrative, “John was drained. He went to mattress early,” “He” refers to “John.”
-
- Within the sentences “John went to the shop. He purchased some milk,” the coreference decision identifies that “He” refers to “John.”
-
- This last part seems to be on the context surrounding a number of sentences and paragraphs to grasp the general movement and which means of the textual content. It’s like analyzing the context across the Lego construction to grasp its function inside a bigger panorama.
-
- Anaphora Decision: This includes figuring out what a pronoun refers to. For instance, in “The canine chased the ball. It was quick,” “it” refers back to the “ball”.
-
- Coherence Evaluation: This step analyzes the logical construction and connections between completely different components of a textual content. It helps the system establish the general message, argument, and intent of the textual content.
7. Textual content Technology
This part includes producing human-like textual content from structured information or primarily based on a given immediate.
-
- Language Modeling: Predicting the subsequent phrase or sequence of phrases given some context (e.g., GPT-3).
-
- Machine Translation: Translating textual content from one language to a different.
-
- Textual content-to-Speech (TTS) and Speech-to-Textual content (STT): Changing written textual content into spoken language or vice versa.
8. Submit-Processing and Analysis
After the principle NLP duties are carried out, outcomes have to be refined and evaluated for high quality.
-
- Analysis Metrics: Measures like accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, BLEU rating (for translation), ROUGE rating (for summarization), and many others., are used to evaluate the efficiency of NLP fashions.
-
- Error Evaluation: Figuring out and understanding errors to enhance mannequin efficiency.
9. Utility/Deployment
Lastly, the NLP mannequin is built-in into real-world functions. This might contain:
-
- Chatbots and Digital Assistants: Purposes like Siri, Alexa, or customer support bots.
-
- Search Engines: Enhancing search relevance by higher understanding queries.
-
- Machine Translation Programs: Computerized language translation instruments (e.g., Google Translate).
-
- Sentiment Evaluation Programs: For analyzing public opinion in social media, opinions, and many others.
-
- Speech Recognition Programs: For changing speech into textual content and vice versa.
10. Machine Studying/Deep Studying Fashions
Reinforcement Studying: Utilized in programs like chatbots the place actions are taken primarily based on consumer interplay.Key Concerns
Description: As soon as the textual content has been processed, varied machine studying or deep studying fashions are used to carry out duties similar to classification, translation, summarization, and query answering.
Supervised Studying: Algorithms are educated on labeled information to carry out duties like sentiment evaluation, classification, or named entity recognition.
Unsupervised Studying: Algorithms are used to search out patterns in unlabeled information, like subject modeling or clustering.
-
- Multilingual NLP: Dealing with textual content in a number of languages and addressing challenges like translation, tokenization, and phrase sense disambiguation.
-
- Bias in NLP: Addressing bias in information and fashions to make sure equity and inclusivity.
-
- Area-Particular NLP: Customizing NLP for specialised fields like medication (bioNLP), regulation (authorized NLP), or finance.
These phases symbolize a typical NLP pipeline, however relying on the applying and downside at hand, not all phases could also be required or carried out in the identical order.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the phases of NLP isn’t only a technical train; it’s a journey into the very coronary heart of how machines are studying to talk our language. As we progress on this area, we’ll proceed unlocking new methods for people and machines to speak and collaborate seamlessly.
Every of those phases performs a vital function in enabling NLP programs to successfully interpret and generate human language. Relying on the duty (like machine translation, sentiment evaluation, and many others.), some phases could also be emphasised greater than others.
Submit Disclaimer
Disclaimer/Writer’s Word: The content material supplied on this web site is for informational functions solely. The statements, opinions, and information expressed are these of the person authors or contributors and don’t essentially mirror the views or opinions of [Your Website Name] The statements, opinions, and information contained in all publications are solely these of the person creator(s) and contributor(s) and never of Lexsense and/or the editor(s). Lexsense and/or the editor(s) disclaim accountability for any harm to folks or property ensuing from any concepts, strategies, directions or merchandise referred to within the content material.