The European Union Synthetic Intelligence Act (EU AI Act) is the primary complete authorized framework to control the design, growth, implementation, and use of AI methods throughout the European Union. The first goals of this laws are to:
- Make sure the secure and moral use of AI
- Shield elementary rights
- Foster innovation by setting clear guidelines— most significantly for high-risk AI purposes
The AI Act brings construction into the authorized panorama for corporations which might be straight or not directly counting on AI-driven options. We want to say that this AI Act is a complete method to AI regulation the world over and can influence companies and builders far past the European Union’s borders.
On this article, we go deep into the EU AI Act: its tips, what corporations could also be anticipated of them, and the higher implications this Act can have on the enterprise ecosystem.
About us: Viso Suite offers an all-in-one platform for corporations to carry out laptop imaginative and prescient duties in a enterprise setting. From individuals monitoring to stock administration, Viso Suite helps clear up challenges throughout industries. To be taught extra about Viso Suite’s enterprise capabilities, ebook a demo with our crew of specialists.
What’s the EU AI Act? A Excessive-Degree Overview
The European Fee printed a regulatory doc in April 2021 to create a uniform legislative framework for the regulation of AI purposes amongst its member states. After greater than three years of negotiation, the legislation was printed on 12 July 2024, going into impact on 1 August 2024.
Following is a four-point abstract of this act:
Danger-based Classification of AI Programs
The danger-based method classifies AI methods into certainly one of 4 threat classes of threat:
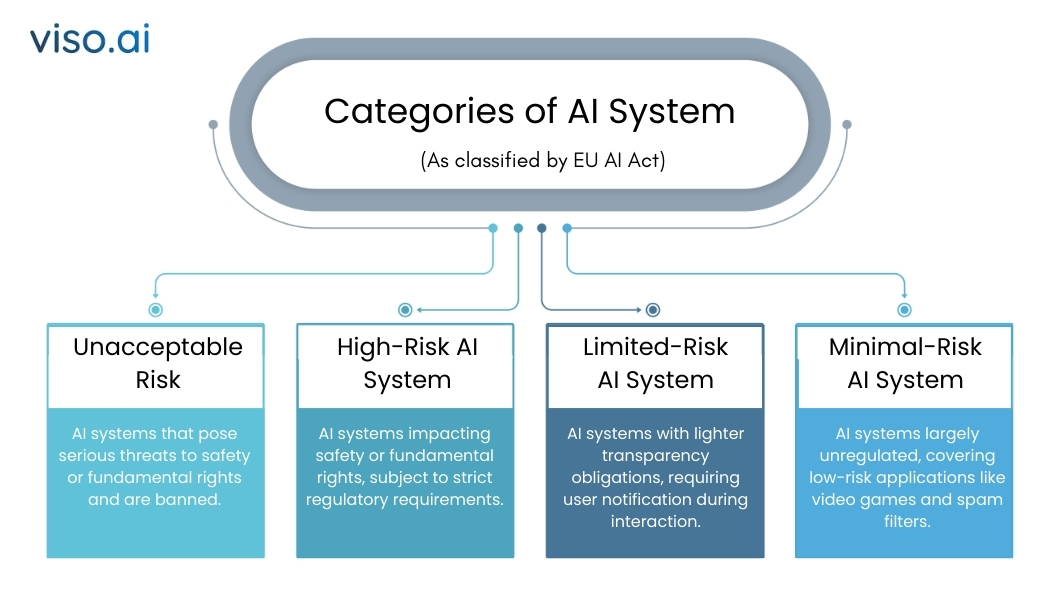

Unacceptable Danger:
AI methods pose a grave hazard and injury to security and elementary rights. This could additionally embody any system making use of social scoring or manipulative AI practices.
Excessive-Danger AI Programs:
This entails AI methods with a direct influence both on security or on primary rights. Examples embrace these within the healthcare, legislation enforcement, and transportation sectors, together with different essential areas. These methods can be topic to essentially the most rigorous regulatory necessities which will embrace rigorous conformity assessments, necessary human oversight, and the adoption of strong threat administration methods.
Restricted Danger:
Programs of restricted threat can have lighter calls for for transparency; nonetheless, builders and deployers ought to be sure that transparency to the end-user is given relating to the presence of AI, for example, chatbots and deepfakes.
Minimal Danger AI Programs:
Most of those methods presently are unregulated, resembling purposes like AI in video video games or spam filters. Nevertheless, as generative AI matures, potential adjustments to the regulatory regime for such methods are usually not precluded.
Obligations on Suppliers of Excessive-Danger AI:
A lot of the compliance burdens builders. In any occasion, whether or not inside or outdoors the EU, these obligations apply to any developer that’s advertising and marketing or working high-risk AI fashions emanating inside or into the European Union states.
Conformity with these laws additional extends to high-risk AI methods offered by third nations whose output is used throughout the Union.


Person’s Obligations (Deployers):
Customers means any pure or authorized individuals deploying an AI system in knowledgeable context. Builders have much less stringent obligations as in comparison with builders. They do, nonetheless, have to make sure that when deploying high-risk AI methods both within the Union or when the output of their system is used within the Union states.
All these obligations are utilized to customers primarily based each within the EU and in third nations.
Basic-Function AI (GPAI):
The builders of general-purpose AI fashions ought to present technical documentation and directions to be used and likewise observe copyright legal guidelines. Their AI Mannequin mustn’t create a systemic threat.
Free and Open-license suppliers of GPAI would adjust to the copyright and publication of the coaching knowledge until their AI mannequin creates a systemic threat.
No matter whether or not being licensed or not, the identical mannequin analysis, adversarial take a look at, incident monitoring and monitoring, and cybersecurity practices must be carried out on GPAI fashions that current systemic dangers.


What Can Be Anticipated From Firms?
Organizations utilizing or creating AI applied sciences must be ready to anticipate vital adjustments in compliance, transparency, and operational oversight. They’ll put together for the next:
Excessive-Danger AI Management Necessities:
Firms deploying high-risk AI methods have to be liable for strict documentation, testing, and reporting. They are going to be anticipated to undertake ongoing threat evaluation, high quality administration methods, and human oversight. We will, in flip, require correct documentation of the system’s performance, security, and compliance. Certainly, non-compliance might entice heavy fines below the GDPR.
Transparency Necessities:
Firms should talk this nicely to customers, whether or not the AI system is obvious sufficient to point to the consumer when he’s coping with an AI system or sufficiently unclear within the case of limited-risk AI. It’s going to therefore enhance consumer autonomy and compliance with the precept of the EU when it comes to transparency and equity. This rule will cowl the usage of issues like deepfakes; they should disclose if a factor is AI-generated or AI-modified.
Knowledge Governance and AI Coaching Knowledge:
Because of this AI methods shall be educated, validated, and examined with numerous, consultant datasets, unbiased in nature. This shall require enterprise to look at extra fastidiously its sources of knowledge and transfer towards much more rigorous types of knowledge governance in order that AI fashions yield nondiscriminatory outcomes.
Affect on Product Growth and Innovation:
The Act introduces AI builders to a higher extent of latest testing and validation procedures which will decelerate the tempo of growth. Firms that may incorporate compliance measures from an early stage of their lifecycle of AI merchandise can have key differentiators in the long term. Strict regulation could curtail the tempo of innovation in AI at first, however companies in a position to modify rapidly to such requirements will discover themselves well-positioned to increase confidently into the EU market.


Pointers to Know About
Firms have to stick to the next key instructions to adjust to the EU Synthetic Intelligence Act:
Timeline for Enforcement
The EU AI Act proposes a phase-in enforcement schedule to provide organizations time to adapt to new necessities.
- 2 August 2024: The official implementation date of the Act.
- 2 February 2025: AI methods falling below the classes of “unacceptable threat” can be banned.
- 2 Might 2025: Codes of conduct apply. These codes are tips to AI builders on greatest practices to adjust to the Act and certainly align their operations with EU rules.
- 2 August 2025: Governance guidelines relating to obligations for Basic Function AI, or GPAI, are in power. For GPAI methods, together with massive language fashions or generative AI, there are explicit calls for on transparency and security. On this respect, the calls for on such methods are usually not interfered with throughout this stage however moderately given time to get ready.
- 2 August 2026: Full implementation of GPAI commitments begins.
- 2 August 2027: Necessities for high-risk AI methods will totally apply, and thus, corporations can have extra time to align with essentially the most demanding components of the regulation.

Danger Administration Programs
The suppliers of high-risk AI have to ascertain a threat administration system offering for fixed monitoring of the efficiency of AIs, periodic assessments regarding compliance points, and the instigation of fallback plans in case any fallacious operation or malfunction of AI methods happens.
Put up-Market Surveillance
Firms can be required to keep up post-market monitoring packages for so long as the AI system is in use. That is to make sure ongoing compliance with the necessities outlined of their purposes. This would come with actions resembling suggestions solicitation, operational knowledge evaluation, and routine auditing.
Human Oversight
The Act requires high-risk AI methods to offer for human oversight. That’s, for example, people want to have the ability to intervene with, or override AI choices, the place that’s mandatory; for example, relating to healthcare, the AI analysis or remedy suggestion must be checked by a healthcare skilled earlier than it’s utilized.
Registration of Excessive-Danger AI Programs
Excessive-risk AI methods have to be registered within the database of the EU and permit entry to the authorities and public with related info relating to the deployment and operation of that AI system.
Third-Social gathering Evaluation
Third-party assessments of some AI methods may very well be wanted earlier than deployment, relying on the danger concerned. Audits, certification, and different types of analysis would verify their conformity with EU laws.
Affect on Enterprise Panorama
The introduction of the EU AI Act is anticipated to have far-reaching results on the enterprise panorama.
Equalizing the Taking part in Discipline
The Act will stage the playground for companies by imposing new laws on AI over corporations of all sizes in issues of security and transparency. This might additionally result in an enormous benefit for smaller AI-driven companies.
Constructing Belief in AI
The brand new EU AI Act will little doubt breed extra client confidence in AI applied sciences by espousing the values of transparency and security inside its provisions. Companies that observe these laws can additional this belief as a differentiator. In flip, advertising and marketing their providers as moral and accountable AI suppliers.
Potential Compliance Prices
For some companies, and particularly smaller ones, the price of compliance may very well be insufferable. Conformity to the brand new regulatory surroundings might nicely require heavy funding in compliance infrastructure, knowledge governance, and human oversight. The fines for non-conformity might go as excessive as 7% of world revenue-a monetary threat corporations can’t afford to miss.
Elevated Accountability in Instances of AI Failure
Companies can be held extra accountable when there’s a failure within the AI system or another misuse that results in injury to individuals or a neighborhood. There can also be a rise within the authorized liabilities of corporations if they don’t take a look at and monitor AI purposes appropriately.
Geopolitical Implications
The EU AI Act lastly can set a globally main instance in regulating AI. Non-EU corporations performing within the EU market are topic to the respective guidelines. Thus, fostering cooperation and alignment internationally with questions of AI requirements. This will additionally name upon different jurisdictions, resembling the US, to take related regulatory steps.


Steadily Requested Questions
Q1. In accordance with the EU AI Act, that are the high-risk AI methods?
A: Excessive-risk AI methods are purposes in fields which have direct contact with a person citizen’s security, rights, and freedoms. This contains AI in essential infrastructures, like transport; in healthcare, like in analysis; in legislation enforcement, enhanced by biometrics; in employment processes; and even in training. These shall be methods of robust compliance necessities, resembling threat evaluation, transparency, and steady monitoring.
Q2. Does each enterprise creating AI should observe the EU AI Act?
A: Not all AI methods are regulated uniformly. Usually, the Act classifies AI methods into the next classes in accordance with their potential for threat. These classes embrace unacceptable threat, excessive, restricted, and minimal threat. This laws solely lays excessive ranges of compliance for high-risk AI methods, primary ranges of transparency for limited-risk methods, and minimal-risk AI methods, which embrace manifestly trivial purposes resembling video video games and spam filters, stay largely unregulated.
Companies creating high-risk AI should comply if their AI is deployed within the EU market, whether or not they’re primarily based inside or outdoors the EU.
Q3. How does the EU AI Act have an effect on corporations outdoors the EU?
A: The EU Synthetic Intelligence Act AI would apply to corporations with a spot of firm outdoors the Union when their AI methods are deployed or used throughout the Union. For example, if an AI system developed in a 3rd nation points outputs used throughout the Union, it then would want to adjust to the necessities below the EU Act. On this vein, all AI methods affecting EU residents would meet the an identical regulatory bar, regardless of the place they’re constructed.
This fall. What are the penalties for any non-compliance with the EU AI Act?
A: The EU Synthetic Intelligence AI Act punishes the occasion of non-compliance with vital fines. Certainly, for extreme infringements, resembling makes use of of prohibited AI methods and non-compliance with obligations for high-risk AI, fines of as much as 7% of the corporate’s general worldwide annual turnover or €35 million apply.
Really helpful Reads
If you happen to get pleasure from studying this text, we’ve got some extra really helpful reads