In This Article
- What are Robotic Joints?
- Anatomy of a Robotic Joint and Functioning
- Kinds of Mechanical Joints
- Management System for Robotic Joints
- Purposes Throughout Industries
Within the ever-evolving panorama of robotics, the place innovation meets precision, the importance of robotic joints can’t be overstated. These mechanical marvels act as the elemental connectors in robotic programs, enabling motion, articulation, and performance much like human movement.
From the swish sweep of a jointed arm robotic to the skilful navigation of a cylindrical robotic, understanding the various varieties, capabilities, and purposes of robotic joints is crucial.
This weblog explores joints, as we unravel the robotic anatomy and discover their capabilities.
What are Robotic Joints?
Robotic joints are the movable connections between totally different components of a robotic’s physique, very similar to the joints in people. These hyperlinks allow robots to bend, twist, and transfer in numerous instructions, permitting them to carry out duties and work together with their setting. Robotic joints are available in many types, together with rotational joints like these in legs and arms, in addition to sliding joints present in robotic grippers and different instruments. These joints are sometimes geared up with actuators, sensors, and mechanical parts to facilitate managed motion and exact positioning. Total, robotic joints are important for the mobility and performance of robots in a variety of purposes, from manufacturing and meeting to exploration and healthcare.
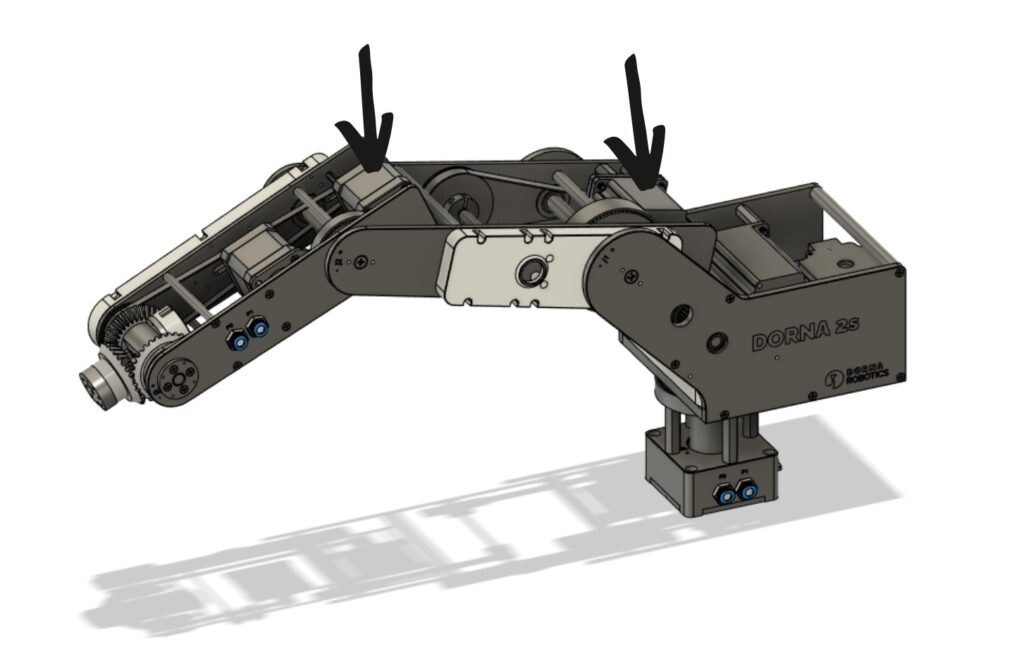
Anatomy of a Robotic Joint and Functioning
A robotic joint is a sort of joint that twists and strikes like a human.
There are mechanical and electrical parts that work collectively to make this occur. By integrating these, robotic joints can obtain a excessive degree of flexibility, accuracy, and effectivity in performing a variety of duties.
This mixture of parts permits robots to imitate the advanced actions of human limbs and perform numerous purposes successfully in industries resembling manufacturing, healthcare, and exploration.
Mechanical Parts
Bearings
Bearings play a significant function in decreasing friction and enabling clean motion inside the joint. They assist the rotation or linear movement of components inside the joint. Widespread kinds of bearings utilized in robotic joints embody ball bearings, curler bearings, and plain bearings. These bearings are sometimes product of sturdy supplies like metal or ceramic and are designed to resist excessive hundreds and speeds whereas minimizing frictional losses.
Linkages
Linkages are mechanical assemblies of rods, bars, and joints that transmit movement and drive between totally different components of the robotic joint. They are often easy, like a single hinge joint, or extra advanced, like a multi-bar linkage mechanism. Linkages permit for managed motion and amplify or cut back the drive utilized to the joint. By rigorously designing the geometry and association of linkages, engineers can obtain particular movement profiles and mechanical benefits tailor-made to the necessities of the robotic’s job.
Gears
Gears are toothed mechanical parts that transmit movement and energy between rotating shafts inside the joint. They’ll change the velocity, torque, or path of rotation, relying on their configuration. Widespread kinds of gears utilized in robotic joints embody spur gears, helical gears, bevel gears, and planetary gears. Gears are important for changing the rotational movement of actuators into the specified motion of the joint. Additionally they present mechanical benefit and management over the joint’s movement, permitting for exact positioning and manipulation.
Electrical Parts
Motors
Electrical motors are the powerhouse behind robotic joints, changing electrical vitality into mechanical movement. These motors are available in numerous varieties, together with DC motors, stepper motors, and servo motors.
DC motors present steady rotation and are generally utilized in purposes the place velocity management is crucial. Stepper motors supply exact management over place and are sometimes utilized in robotic programs requiring correct positioning. Servo motors mix the options of each DC and stepper motors, providing exact management over each velocity and place. The selection of the robotic arm joint motor is dependent upon components such because the required torque, velocity, and precision of motion wanted for the precise software of the robotic joint.
Sensors
Sensors play an important function in offering suggestions to the robotic’s management system, enabling it to watch and regulate the joint’s place, velocity, and drive precisely. Encoders are generally used to measure the rotational place of the joint, offering exact suggestions for controlling motion.
Potentiometers measure the angle of rotation, whereas load cells gauge the drive exerted by the joint. Moreover, proximity sensors detect the presence of objects within the joint’s neighborhood, enhancing security and stopping collisions. By integrating numerous kinds of sensors, robotic joints can function with precision and reply dynamically to adjustments of their setting, guaranteeing environment friendly and secure operation.
Management Methods
The management system acts because the central nervous system of the robotic joint, orchestrating the interplay between sensors, actuators, and different parts. It processes the suggestions from sensors to find out the joint’s present state and calculates the required instructions to attain the specified motion.
Proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controllers are generally used algorithms to control the joint’s place, velocity, and drive precisely. Superior management strategies, resembling fuzzy logic and neural networks, can improve the adaptability and robustness of the management system, enabling the robotic joint to carry out advanced duties in numerous environments. By exact coordination and suggestions mechanisms, the management system ensures that the robotic joint operates easily, effectively, and safely, assembly the calls for of numerous purposes.

Kinds of Mechanical Joints
Within the dynamic realm of robotics, selecting the suitable joint sort holds the utmost significance in attaining desired functionalities and optimizing efficiency throughout numerous purposes. Robotic joints are available in numerous types, every with distinct traits, purposes, and benefits. Let’s delve into the categorization of robotic joints and discover their significance:
Revolute Joints
Traits: Revolute joints, also called rotary joints, facilitate rotation round a single axis. They provide versatility in motion and are pivotal in enabling bending and twisting motions.
Purposes: Revolute joints discover in depth use in robotic legs and arms, the place they permit articulation and maneuverability important for duties resembling meeting, welding, and materials dealing with in manufacturing processes.
Benefits: The flexibility of revolute joints permits for a variety of movement, making them appropriate for purposes requiring flexibility and adaptableness in motion.
Prismatic Joints
Traits: Prismatic joints, additionally known as linear joints, allow motion alongside a single axis in a straight line. They excel in offering exact linear movement.
Purposes: Prismatic joints are generally employed in robotic sliders, extendable arms, and telescopic mechanisms, the place exact linear motion is essential for duties resembling pick-and-place operations and positioning.
Benefits: Prismatic joints supply exact management over linear movement, making them perfect for purposes requiring correct positioning and alignment.
Spherical Joints
Traits: Spherical joints, also called ball-and-socket joints, permit motion in a number of instructions round a central level. They provide a excessive diploma of flexibility in movement.
Purposes: Spherical joints are generally utilized in robotic wrists and hips, the place omnidirectional motion is crucial for duties resembling object manipulation, greedy, and navigation in advanced environments.
Benefits: The flexibleness supplied by spherical joints permits robots to navigate and work together with their environment extra successfully, making them appropriate for purposes requiring agility and adaptableness.
Common Joints
Traits: Common joints, additionally referred to as cardan joints, facilitate rotation round two non-intersecting axes. They provide flexibility in altering the orientation of linked components.
Purposes: Common joints are sometimes employed in robotic manipulators and drive shafts to transmit movement between misaligned parts, permitting for clean and environment friendly operation in numerous industrial purposes.
Benefits: The power of common joints to accommodate misalignment enhances the maneuverability and effectivity of robotic programs, significantly in duties requiring advanced movement trajectories.
Cylindrical Joints
Traits: Cylindrical joints mix rotational and linear movement alongside a single axis, comprising a revolute joint coupled with a prismatic joint.
Purposes: Cylindrical joints are generally present in cylindrical robotic arms and grippers, the place duties necessitate each rotational and linear motion, resembling materials dealing with, machining, and meeting operations.
Benefits: The mixing of rotational and linear movement in cylindrical joints affords versatility in performing duties that require a mixture of each kinds of motion, enhancing the effectivity and performance of robotic programs.
Planar Joints
Traits: Planar joints allow motion inside a single airplane outlined by two perpendicular axes, proscribing movement to two-dimensional house.
Purposes: Planar joints are well-suited for purposes requiring exact movement management in a flat airplane, resembling robotic sliders, rotary phases, and XY positioning programs utilized in manufacturing, semiconductor, and biomedical industries.
Benefits: Planar joints present correct and environment friendly movement management in two-dimensional house, making them indispensable for duties that demand exact positioning and alignment.
Choosing the appropriate sort of joint is essential in designing robotic programs tailor-made to particular purposes and necessities. By understanding the traits, purposes, and benefits of several types of robotic joints, engineers can optimize the efficiency and performance of robotic programs throughout numerous industries, driving innovation and effectivity within the subject of robotics. Whether or not it’s revolutionizing manufacturing processes, enhancing healthcare outcomes, or optimizing logistical operations, the flexibility and adaptableness of robotic joints play a pivotal function in shaping the way forward for automation and robotics.

Management System for Robotic Joints
The management system for robotic joints is the mind behind their motion, chargeable for decoding sensor suggestions and sending instructions to actuators to control place, velocity, and torque. It contains sensors, a controller, and actuators working collectively to make sure exact and environment friendly movement management.
Closed-loop Management
In a closed-loop management system, sensors repeatedly monitor the joint’s place, velocity, and different related parameters and supply suggestions to the controller.
The controller compares this suggestions with the specified setpoint and generates corrective indicators to regulate the joint’s motion accordingly. This suggestions loop permits for real-time changes, guaranteeing that the joint follows the specified trajectory precisely regardless of exterior disturbances or variations in load.
Closed-loop management programs supply excessive accuracy and stability, making them perfect for purposes requiring exact positioning and movement management, resembling robotic surgical procedure and manufacturing processes.
Trusted manufacturers like Dorna present closed-loop management in all their robots for utmost security.
Open-loop Management
Open-loop management programs function with out suggestions from sensors.
As an alternative, the controller generates predetermined instructions primarily based solely on the specified trajectory and timing. These instructions are despatched on to the actuators with out monitoring the precise efficiency of the joint.
Whereas open-loop management programs are easier and more cost effective to implement, they’re inherently much less correct and fewer strong to disturbances in comparison with closed-loop programs. They’re appropriate for purposes the place exact movement management isn’t essential, resembling easy pick-and-place duties in meeting traces or primary movement sequences in leisure robotics.
Purposes Throughout Industries
The flexibility and adaptableness of robotic joints make them indispensable throughout a variety of industries and purposes.
Amica Applied sciences efficiently carried out the Dorna robotic arm to automate guide duties. Watch how.
In manufacturing, robots geared up with jointed arms and rotary joints automate duties resembling meeting, welding, and materials dealing with, rising productiveness and effectivity.
In healthcare, robotic programs with specialised joints allow minimally invasive surgical procedures, enhancing affected person outcomes and decreasing restoration instances.
From logistics and warehousing to agriculture, building, and leisure, robotic joints play a pivotal function in revolutionizing industries and driving innovation ahead.
Dorna is a one-stop store for industrial automation options. It affords a sequence of quick, correct, and agile robots which might be the perfect resolution for versatile and compact automation. Discover robotic equipment to swimsuit the various wants of companies to the final element.
Discover Dorna’s software in your warehouse processes.