The training curve is one other key idea that’s utilized to measure the facets of expertise and effectivity beneficial properties in time. The training curve is an idea that applies to the manufacturing course of, coaching, and any operation that includes a talent in realizing that the time or value of the unit or job lowering with a rise within the variety of models or duties completed. First, the speed of improve throughout the first models is steep, however the charge drops to a gentle slope, after which to a horizontal line. Evaluation of the educational curve affords businesspersons vital insights into the optimization of manufacturing programs, value management, and coaching methods.
Studying Targets
- Perceive the idea and significance of the educational curve in varied industries.
- Discover ways to calculate and apply the educational curve formulation to real-world situations.
- Analyze the affect of the educational curve on manufacturing effectivity and price discount.
- Discover various factors influencing the form and steepness of a studying curve.
- Develop abilities to visualise and interpret studying curves utilizing knowledge evaluation instruments.
What’s Studying Curve?
The training curve represents the phenomenon the place the time or value of finishing a job decreases as expertise will increase. In easier phrases, as individuals or organizations carry out a job repeatedly, they turn out to be extra environment friendly at it, and that is mirrored in diminished time or value per unit of output.
A typical studying curve is generally characterised by an preliminary stage the place modifications are steep due to the rising understanding of how a sure job is to be executed. Extending the curve to the proper we get a curve that’s flattened as additional enchancment turn out to be marginal indicating that the duty has turn out to be routine and there may be little to be gained.
Key ideas associated to the educational curve embody:
- Preliminary Studying Part: The stage the place people or organizations are most inefficient, and the curve is steep.
- Plateau or Diminishing Returns: After preliminary speedy studying, additional progress slows down, inflicting the curve to flatten.
- Cumulative Expertise: The overall variety of models produced or the full period of time spent on the duty, straight influencing the development charge.
Kinds of Studying Curves
There are a number of variations of the educational curve that replicate totally different charges of enchancment. These curves may be categorized into three fundamental sorts:
- Steep Studying Curve: The preliminary section of the curve is steep, indicating speedy studying and important enchancment in efficiency or effectivity. One of these curve happens when duties are initially unfamiliar, and persons are extremely motivated to be taught.
- Instance: A newbie studying a brand new software program instrument or an organization organising a brand new manufacturing course of would possibly expertise a steep studying curve as they rapidly turn out to be proficient.
- Shallow Studying Curve: The training curve is flatter, indicating slower enhancements. This happens when the duty is comparatively easy or when the learner has prior data or abilities associated to the duty.
- Instance: An skilled employee studying a small variation in an current course of would possibly expertise solely modest beneficial properties as the brand new job requires minimal adjustment.
- Flat Studying Curve: In some circumstances, after a interval of speedy enchancment, the curve flattens out, indicating that additional studying turns into incremental, with little or no enchancment in efficiency. This usually happens when most proficiency has been reached.
- Instance: A high-level professional in a subject would possibly face a flat studying curve, as the duty turns into so routine that additional progress is extraordinarily troublesome.
Significance of Understanding the Studying Curve
Understanding the educational curve is essential for a number of causes, because it helps organizations, companies, and people optimize sources, plan successfully, and enhance effectivity. Listed here are some key factors highlighting its significance:
- Value Discount: By recognizing how time or prices lower as expertise will increase, companies can predict value financial savings over time. The training curve permits firms to estimate the discount in manufacturing prices as staff achieve extra experience and processes turn out to be streamlined.
- Effectivity Optimization: Understanding the educational curve helps establish areas the place processes may be optimized, enabling companies to enhance productiveness and obtain increased output with much less time and effort.
- Forecasting and Planning: The training curve offers a dependable instrument for forecasting future efficiency. It helps organizations plan for long-term development, decide when effectivity will plateau, and handle useful resource allocation successfully.
- Enhancing Coaching Packages: In talent improvement and worker coaching, understanding the educational curve helps organizations design more practical coaching applications. It permits companies to anticipate how rapidly workers will achieve proficiency and helps in setting sensible efficiency objectives.
- Strategic Resolution-Making: By understanding how studying and effectivity enhance over time, companies could make higher strategic choices about scaling manufacturing, introducing new merchandise, or investing in applied sciences that improve studying charges.
- Aggressive Benefit: Corporations that perceive and apply the educational curve can achieve a aggressive edge by lowering prices and rising manufacturing velocity quicker than their opponents. This understanding may also assist firms keep forward when it comes to innovation and technological adoption.
Working of Studying Curve
The training curve works on the precept that as a person, workforce, or system repeats a job or course of, they turn out to be extra environment friendly over time. Initially, the time or value required to provide the primary unit is excessive on account of unfamiliarity with the duty. Nonetheless, as extra models are produced or duties are carried out, effectivity will increase, leading to a lower within the time or value per unit. This phenomenon happens on account of diminished errors, improved strategies, quicker decision-making, and higher utilization of sources.
The training curve sometimes follows a predictable sample the place the speed of enchancment is speedy at first however slows down over time as the duty turns into extra acquainted. Over time, the curve ranges off, indicating that additional enhancements will probably be marginal as the duty turns into routine.
Key Variables within the Studying Curve
- Preliminary Time (a): That is the time or value required to provide the primary unit or full the primary job. It represents the place to begin on the educational curve and is often the best worth due to inefficiencies and inexperience.
- Studying Curve Index (b): The training curve index (b) represents the speed at which effectivity improves as extra models are produced or duties are accomplished. A unfavourable worth of b signifies a lower in time or value, and its magnitude determines how rapidly effectivity will increase. A steeper curve (extra unfavourable b) suggests quicker studying and larger enhancements early on. A shallower curve (much less unfavourable b) signifies slower studying and enhancements.
- Variety of Items or Duties (X): This refers back to the variety of models produced or duties accomplished over time. Because the quantity (X) will increase, the time or value per unit decreases, illustrating the affect of repeated observe or manufacturing. The connection between time and the variety of models follows a lowering exponential perform.
- Time or Value per Unit (Y): That is the dependent variable on the educational curve, representing the time or value wanted to provide every unit or full every job. As expertise will increase, the time or value required per unit decreases.
Studying Curve Components
The mathematical relationship that describes how time or value decreases with elevated expertise is commonly represented by the formulation:
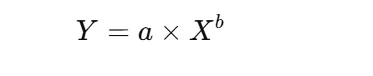
The place:
- Y = Time or value to provide the Xth unit
- a = Time or value to provide the primary unit (preliminary time)
- X = Cumulative variety of models or duties produced
- b = Studying curve index, which dictates the speed of enchancment
This formulation helps in calculating the anticipated time or value for any unit quantity (X) based mostly on the preliminary time and the educational curve index. By plotting the curve, companies can visually monitor how their effectivity improves over time.
Studying Curve Calculation Instance:
Think about an organization is producing widgets, and the time to provide the primary unit is 100 hours. Primarily based on historic knowledge, the corporate has decided that the educational curve index b is -0.3, which means that with every doubling of manufacturing, the time required to provide every unit decreases by 30%.
We are able to calculate the time to provide the fifth unit as follows:
- a = 100 hours (time for the primary unit)
- b = -0.3
- X = 5 (we need to know the time for the fifth unit)
The formulation is:
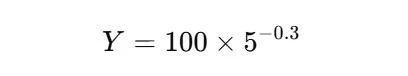
Calculating the exponent:
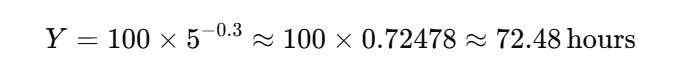
So, the time to provide the fifth unit is roughly 72.48 hours.
Deciphering the Components:
- When X = 1 (the primary unit):
The formulation simplifies to Y = a, which means the time or value for the primary unit is the preliminary worth (a). - As X will increase:
The exponent b ensures that the time or value decreases. The bigger the variety of models produced, the nearer the time or value will get to its minimal worth.
Studying Curve and Doubling of Manufacturing
A generally used rule within the studying curve idea is the doubling rule, which states that each time the variety of models produced doubles, the time or value required to provide every unit decreases by a set share. This relationship is mirrored within the studying curve equation, the place the exponent b governs how rapidly this discount occurs. For instance, a 20% studying curve implies that each time manufacturing doubles, the time per unit decreases by 20%.
Logarithmic Type of the Studying Curve
In observe, the educational curve equation is commonly remodeled right into a logarithmic type to simplify evaluation, particularly when coping with massive datasets.
The logarithmic type is:
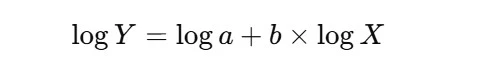
By taking the logarithm of each side, we are able to linearize the curve, which makes it simpler to estimate the parameters a and b from real-world knowledge by regression evaluation.
This transformation is especially helpful when analyzing large-scale manufacturing knowledge, because it converts the exponential decay right into a straight line, making it simpler to interpret and forecast.
Implementation and Instance of the Studying Curve
The training curve may be applied utilizing the mathematical mannequin we mentioned earlier. Beneath, I’ll stroll by an instance of tips on how to calculate and visualize the educational curve in a sensible situation, resembling manufacturing a product. We are going to use Python to implement this mannequin.
Step-by-Step Implementation
State of affairs: Suppose an organization is manufacturing widgets, and the time to provide every widget decreases as extra widgets are produced. The time to make the primary widget is 50 minutes, and the educational curve index (b) is -0.3. We need to calculate and plot the time it takes to provide every widget over a collection of 20 widgets.
Step1: Importing Essential Libraries
We are going to want libraries like numpy for numerical computations and matplotlib for plotting the graph.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltStep2: Outline the Studying Curve Components
As talked about earlier, the educational curve is represented by the formulation:
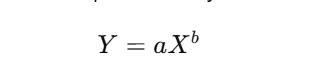
The place:
- Y is the time taken for the Xth unit.
- a is the time to provide the primary unit (50 minutes).
- X is the variety of models produced.
- b is the educational curve index (-0.3).
def learning_curve(a, b, X):
return a * X**bStep3: Calculate Time for A number of Items
Let’s calculate the time taken for every unit from 1 to twenty.
# Parameters
a = 50 # Time for the primary unit (in minutes)
b = -0.3 # Studying curve index
# Generate the variety of models produced (X)
models = np.arange(1, 21) # 1 to twenty models
# Calculate the time to provide every unit
instances = learning_curve(a, b, models)
# Print the instances for every unit
for unit, time in zip(models, instances):
print(f"Time to provide unit {unit}: {time:.2f} minutes")Step4: Plotting the Studying Curve
Now that now we have the info, we are able to visualize the educational curve by plotting the time taken to provide every unit.
# Plotting the educational curve
plt.determine(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(models, instances, marker="o", colour="b", linestyle="-", label="Studying Curve")
plt.title('Studying Curve: Time to Produce Widgets')
plt.xlabel('Variety of Items Produced')
plt.ylabel('Time to Produce Every Unit (Minutes)')
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.present()Output:
Time to provide unit 1: 50.00 minutes
Time to provide unit 2: 40.61 minutes
Time to provide unit 3: 35.96 minutes
Time to provide unit 4: 32.99 minutes
Time to provide unit 5: 30.85 minutes
Time to provide unit 6: 29.21 minutes
Time to provide unit 7: 27.89 minutes
Time to provide unit 8: 26.79 minutes
Time to provide unit 9: 25.86 minutes
Time to provide unit 10: 25.06 minutes
Time to provide unit 11: 24.35 minutes
Time to provide unit 12: 23.73 minutes
Time to provide unit 13: 23.16 minutes
Time to provide unit 14: 22.65 minutes
Time to provide unit 15: 22.19 minutes
Time to provide unit 16: 21.76 minutes
Time to provide unit 17: 21.37 minutes
Time to provide unit 18: 21.01 minutes
Time to provide unit 19: 20.67 minutes
Time to provide unit 20: 20.35 minutes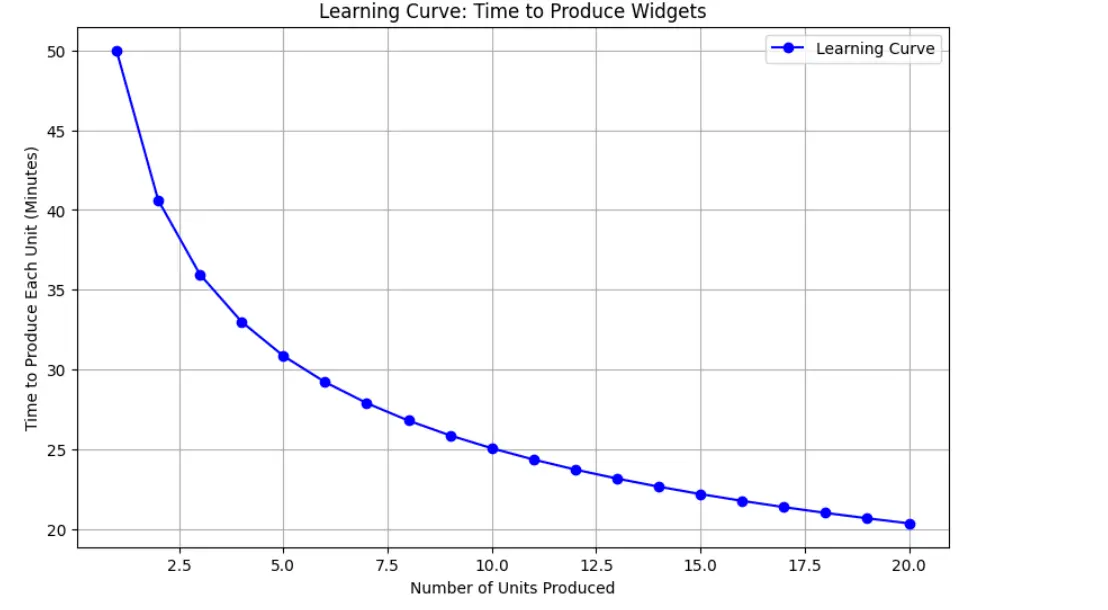
Significance of Studying Curve
Allow us to find out about significance of studying curve under:
- Complexity of the Process: Extra advanced duties take longer to grasp, slowing down the educational curve. Less complicated, repetitive duties have a tendency to point out faster enhancements.
- Employee Ability and Expertise: Expert staff be taught quicker on account of prior data and experience. Efficient coaching additionally accelerates studying by offering structured steering.
- Technological Advances: New instruments and automation can scale back job time and improve studying effectivity. Superior applied sciences velocity up processes and decrease error charges.
- Quantity of Manufacturing: Repetition boosts effectivity, with every further unit taking much less time. Batch manufacturing can decelerate studying on account of irregular publicity.
- Work Atmosphere and Organizational Components: Collaborative and supportive work environments velocity up studying. Robust management and good morale additionally encourage quicker talent acquisition.
- Suggestions and Studying from Errors: Well timed suggestions helps staff appropriate errors rapidly, dashing up studying. A tolerant surroundings for errors fosters steady enchancment.
Conclusion
The training curve is a robust instrument for understanding how effectivity improves over time by expertise and repetition. It’s also an important instrument for companies to optimize processes, forecast value reductions, and allocate sources successfully. It applies throughout industries, from manufacturing to talent improvement, emphasizing the diminishing returns of enchancment as expertise grows. By understanding and leveraging the educational curve, organizations can improve productiveness, plan strategically, and deal with the challenges of scaling operations or refining efficiency over time.
Key Takeaways
- The training curve reveals how effectivity improves with repeated observe or manufacturing.
- Preliminary progress is speedy, however the charge of enchancment slows over time.
- Studying curve evaluation helps predict value financial savings and manufacturing time reductions.
- The curve’s form is influenced by elements just like the complexity of duties and studying charges.
- Understanding the educational curve aids in strategic planning and optimizing sources.
Ceaselessly Requested Questions
A: The training curve is a graphical illustration exhibiting how effectivity improves as expertise or manufacturing will increase, with time or value sometimes lowering as extra models are produced.
A: The curve flattens as enhancements turn out to be much less important with every further unit produced, indicating diminishing returns within the studying course of.
A: Companies use the educational curve to estimate manufacturing prices, forecast effectivity enhancements, and optimize sources for long-term planning.
A: Components resembling job complexity, employee talent degree, coaching, and know-how can affect how rapidly effectivity improves and the way steep the educational curve is.
A: Sure, the educational curve applies to talent improvement as effectively, exhibiting how rapidly an individual improves at a job over time with observe and expertise.