Introduction
Think about you might be conducting a research to find out whether or not a brand new drug successfully reduces blood strain. You administer the drug to a gaggle of sufferers and examine their outcomes to a management group receiving a placebo. You analyze the info and conclude that the brand new drug considerably reduces blood strain when, in actuality, it doesn’t. This incorrect rejection of the null speculation (that the drug has no impact) is a Kind I error. Alternatively, suppose the drug truly does scale back blood strain, however your research fails to detect this impact on account of inadequate pattern measurement or variability within the information. Because of this, you conclude that the drug is ineffective, which is a failure to reject a false null speculation—a Kind II error.
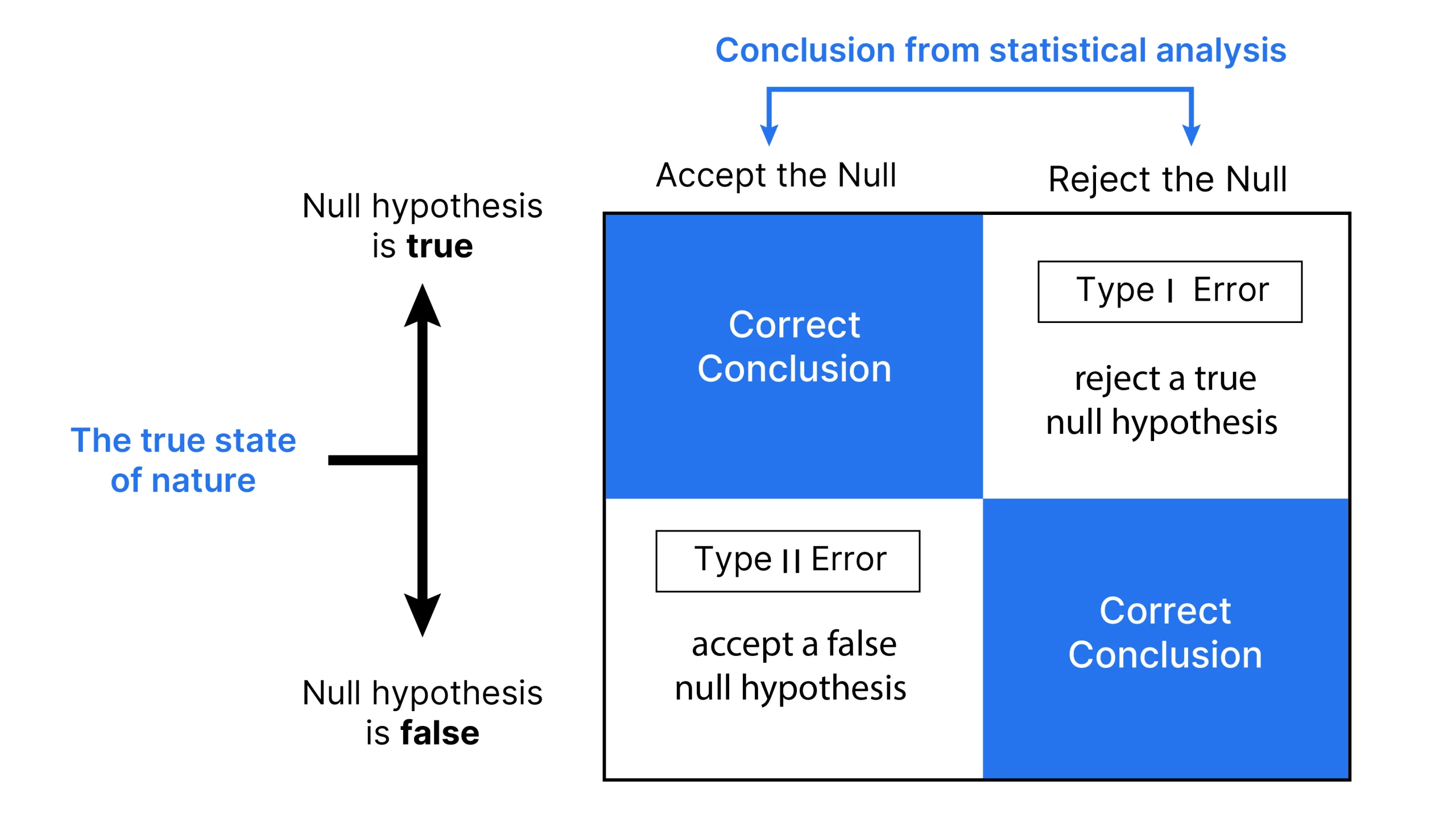
These eventualities spotlight the significance of understanding Kind I and Kind II errors in statistical testing. Kind I errors, also referred to as false positives, happen once we mistakenly reject a real null speculation. Kind II errors, or false negatives, occur once we fail to reject a false null speculation. A lot of statistical principle revolves round minimizing these errors, although fully eliminating each is statistically inconceivable. By understanding these ideas, we will make extra knowledgeable choices in varied fields, from medical testing to high quality management in manufacturing.
Overview
- Kind I and Kind II errors characterize false positives and false negatives in speculation testing.
- Speculation testing entails formulating null and various hypotheses, selecting a significance degree, calculating take a look at statistics, and making choices based mostly on important values.
- Kind I errors happen when a real null speculation is mistakenly rejected, resulting in pointless interventions.
- Kind II errors occur when a false null speculation will not be rejected, inflicting missed diagnoses or neglected results.
- Balancing Kind I and Kind II errors entails trade-offs in significance ranges, pattern sizes, and take a look at energy to reduce each errors successfully.
The Fundamentals of Speculation Testing
Speculation testing is a technique used to determine whether or not there’s sufficient proof to reject a null speculation (H₀) in favor of another speculation (H₁). The method entails:
- Formulating Hypotheses
- No impact or no distinction: No impact or no distinction.
- Different Speculation (H₁): An impact or a distinction exists.
- Selecting a Significance Degree (α): The chance threshold for rejecting H₀, usually set at 0.05, 0.01, or 0.10.
- Calculating the Take a look at Statistic: A worth derived from pattern information used to check in opposition to a important worth.
- Making a Choice: If the take a look at statistic exceeds the essential worth, reject H₀; in any other case, don’t reject H₀.
Additionally learn: Finish-to-Finish Statistics for Knowledge Science
Kind 1 Error( False Optimistic)
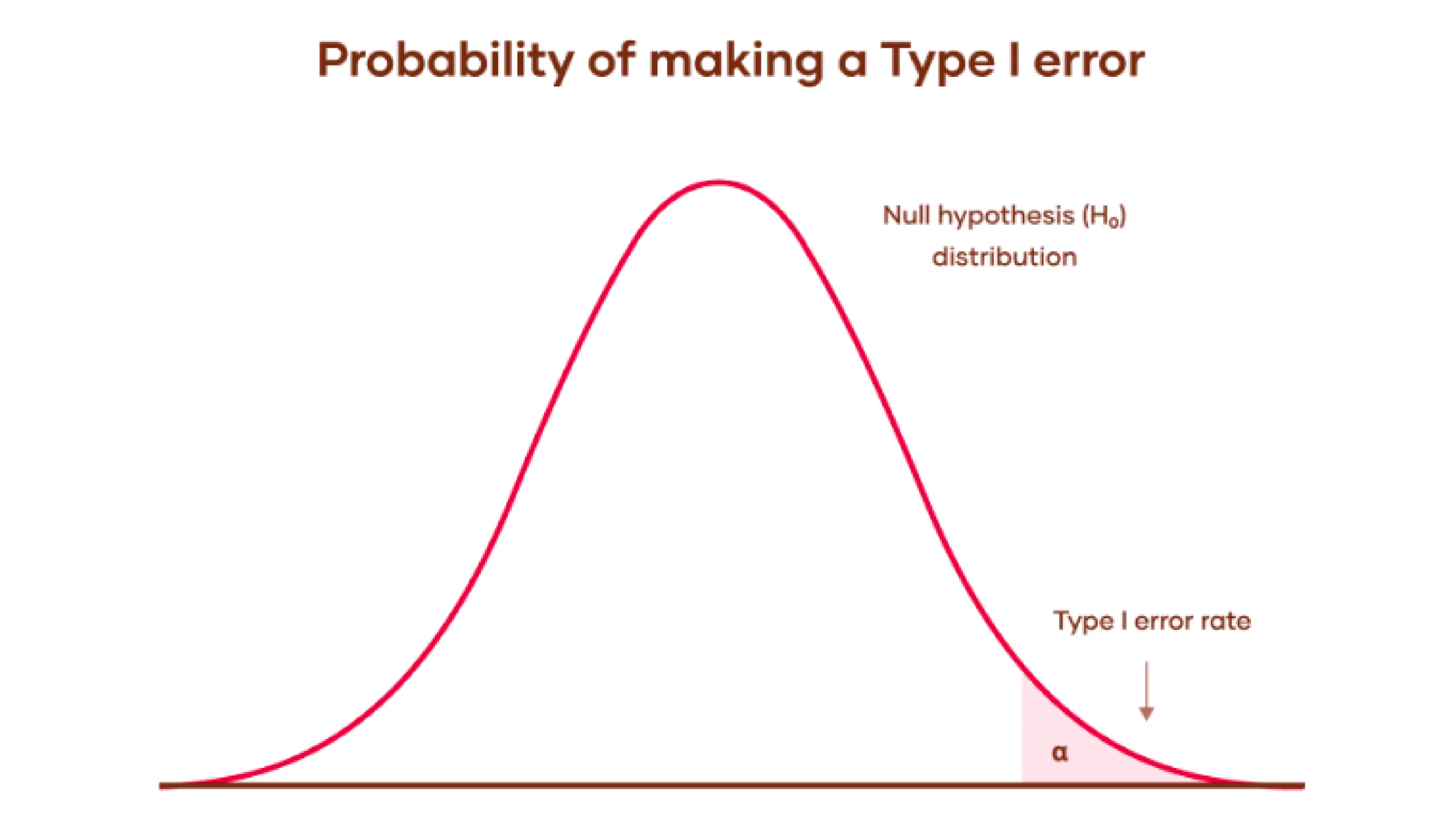
A Kind I error happens when an experiment’s null speculation(H0) is true however mistakenly rejected (the Graph is talked about beneath).
This error represents figuring out one thing that’s not truly current, just like a false constructive. This may be defined in easy phrases with an instance: In a medical take a look at for a illness, a Kind I error would imply the take a look at signifies a affected person has the illness when they don’t, primarily elevating a false alarm. On this case, the null speculation(H0) would state: The affected person doesn’t have illness.
The probability of committing a Kind I error known as the importance degree or charge degree. It’s denoted by the Greek letter α (alpha) and is called the alpha degree. Sometimes, this opportunity or chance is about at 0.05 or 5%. This fashion, researchers are often inclined to just accept a 5% likelihood of incorrectly rejecting the null speculation when it’s sincerely precise.
Kind I errors can result in pointless therapies or interventions, inflicting stress and potential hurt to people.
Let’s perceive this with Graph:
- Null Speculation Distribution: The bell curve exhibits the vary of potential outcomes if the null speculation is true. This implies the outcomes are on account of random likelihood with none precise impact or distinction.
- Kind I Error Price: The shaded space beneath the curve’s tail represents the importance degree, α. It’s the chance of rejecting the null speculation when it’s truly true. Which ends up in a Kind I error (false constructive).
Kind 2 Error ( False Unfavourable)
A Kind II error occurs when a legitimate various speculation goes unrecognized. In less complicated phrases, it’s like failing to identify a bear that’s truly there, thus not elevating an alarm when one is required. On this situation, the null speculation (H0) nonetheless states, “There isn’t a bear.” The investigator commits a Kind II error if a bear is current however undetected.
The important thing issue isn’t all the time whether or not the illness exists however whether or not it’s successfully identified. The error can come up in two methods: both by failing to find the illness when it’s current or by claiming to find the illness when it isn’t current.
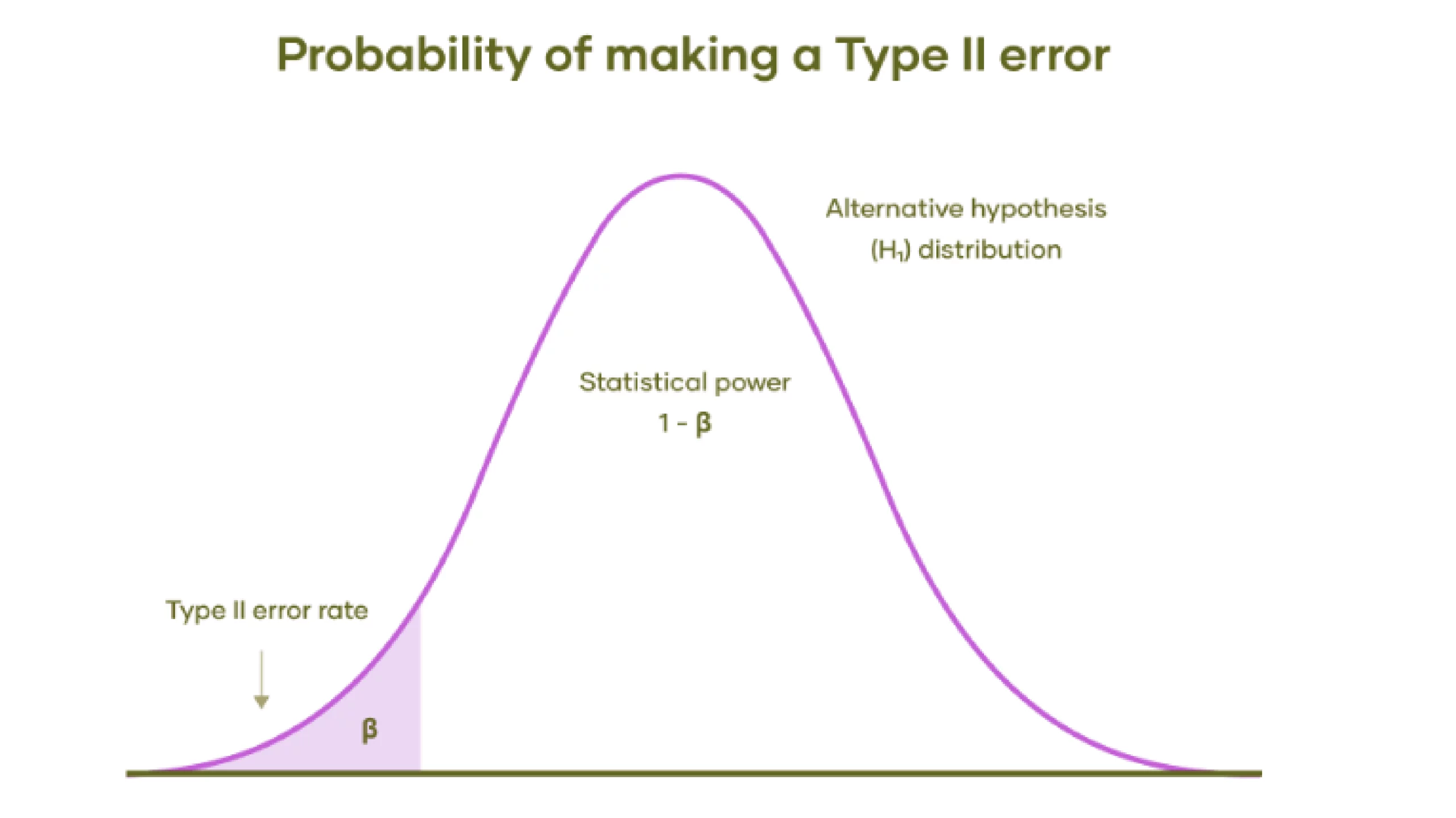
The chance of Kind II error is denoted by the Greek letter β (beta). This worth is expounded to a take a look at’s statistical energy, which is calculated as 1 minus β (1−β).
Kind II errors may end up in missed diagnoses or neglected results, resulting in insufficient therapy or interventions.
Let’s perceive this with Graph:
- Different Speculation Distribution: The bell curve represents the vary of potential outcomes if the choice speculation is true. This implies there’s an precise impact or distinction, opposite to the null speculation.
- Kind II Error Price (β): The shaded space beneath the left tail of the distribution represents the chance of a Kind II error.
- Statistical Energy (1 – β): The unshaded space beneath the curve to the fitting of the shaded space represents the take a look at’s statistical energy. Statistical energy is the chance of appropriately rejecting the null speculation when the choice speculation is true. Larger energy means a decrease likelihood of constructing a Kind II error.
Additionally learn: Be taught all About Speculation Testing!
Comparability of Kind I and Kind II Errors
Right here is the detailed comparability:
| Side | Kind I Error | Kind II Error |
|---|---|---|
| Definition and Terminology | Rejecting a real null speculation (false constructive) | Accepting a false null speculation (false destructive) |
| Symbolic Illustration | α (alpha) | β (beta) |
| Likelihood and Significance | Equal to the extent of significance set for the take a look at | Calculated as 1 minus the facility of the take a look at (1 – energy) |
| Error Discount Methods | Lower the extent of significance (will increase Kind II errors) | Improve the extent of significance (raises Kind I errors) |
| Causal Elements | Probability or luck | Smaller pattern sizes or much less highly effective statistical exams |
| Analogies | “False hit” in a detection system | “Miss” in a detection system |
| Speculation Affiliation | Incorrectly rejecting the null speculation | Failing to reject a false null speculation |
| Prevalence Situations | Happens when acceptance ranges are too lenient | Happens when acceptance standards are overly stringent |
| Implications | Prioritized in fields the place avoiding false positives is essential (e.g., medical testing) | Prioritized in fields the place avoiding false negatives is essential (e.g., screening for extreme ailments) |
Additionally learn: Speculation Testing Made Simple for Knowledge Science Newcomers
Commerce-off Between Kind I and Kind II Errors
There may be largely a trade-off amongst Kind I and Kind II errors. Decreasing the probability of 1 kind of error typically will increase the chance for the other.
- Significance Degree (α): Decreasing α reduces the prospect of a Kind I error however will increase the chance of a Kind II error. Growing α has the other impact.
- Pattern Measurement: Growing the pattern measurement can scale back each Kind I and Kind II errors, as bigger samples present extra correct estimates.
- Take a look at Energy: Enhancing the take a look at’s energy by rising the pattern measurement or utilizing extra delicate exams can scale back the chance of Kind II errors.
Conclusion
Kind I and Kind II errors are basic concepts in statistics and analysis strategies. By realizing the distinction between these errors and their implications, we will interpret analysis findings higher, conduct extra highly effective analysis, and make extra knowledgeable choices in numerous fields. Keep in mind, the purpose isn’t to get rid of errors (which is inconceivable) however to handle them efficiently based mostly on the actual context and potential outcomes.
Steadily Requested Questions
Ans. It’s difficult to get rid of each kinds of errors as a result of lowering one usually will increase the opposite. Nevertheless, by rising the pattern measurement and thoroughly designing the research, researchers can lower each errors to relevant ranges.
Ans. Listed below are the frequent misconceptions about Kind I and Kind II errors:
False impression: A decrease α all the time means a greater take a look at.
Actuality: Whereas a decrease α reduces Kind I errors, it will possibly enhance Kind II errors, resulting in missed detections of true results.
False impression: Massive pattern sizes get rid of the necessity to fear about these errors.
Actuality: Massive pattern sizes scale back errors however don’t get rid of them. Good research design continues to be important.
False impression: A major outcome (p-value < α) means the null speculation is fake.
Actuality: A major outcome suggests proof in opposition to H₀, however it doesn’t show H₀ is fake. Different components like research design and context have to be thought-about.
Ans. Growing the facility of your take a look at makes it extra prone to detect a real impact. You are able to do this by:
A. Growing your pattern measurement.
B. Utilizing extra exact measurements.
C. Decreasing variability in your information.
D. Growing the impact measurement, if potential.
Ans. Pilot research allow you to estimate the parameters wanted to design a bigger, extra definitive research. They supply preliminary information on impact sizes and variability, which inform your pattern measurement calculations and assist stability Kind I and Kind II errors in the primary research.